Hi Everyone - There is a message on my home page re the future of this site.
Yr 12 CHEMISTRY - Units 3 and 4
Units 3 and 4 of the QCAA Chemistry syllabus. Topics of redox, acids/bases, equilibrium, and organic Chemistry.Course overview Overview - weeks/topics for Units 3 and 4 (including assessment)
Unit 3 Topics: Learning Goals and Success Criteria
- 1. Redox reactions
- 7. Equilibrium Constants
- 2. Electrochemical cells
- 8. Acids and Bases
- 3. Galvanic Cells
- 9. Volumetric Analysis
- 4. Std Electrode Pot
- 10. pH Scale
- 5. Chemical equilibrium
- 11. Dissociation Constants
- 6. Factors affecting Equilibrium
- 12. Acid/Base Indicators
Student Experiment Task Sheet - and guide to writing a great report.
Research Assignment Task Sheet + two guides (simple and detailed) to writing a great report.
Unit 4 Topics: Learning Goals and Success Criteria
There are four summative assessment items in year 12. The two assessment items in Unit 3 are a Data Test (10%) and Student Experiment (20%). The two assessment items in Unit 4 are a Student Research Investigation (20%) and external Examination (50%). There is approximately one assessment item per term, although the yr 12 course is not aligned with school terms.
UNIT 3
![]() Unit 3 Learning Goals and Success Criteria
Unit 3 Learning Goals and Success Criteria
1. Redox Reactions
Unit 3 Topic 2 (Yr 11 Week 34,35 6 lessons)
![]() Introduction to REDOX notes - a one pager with some intro notes. Edited from CK-12
Introduction to REDOX notes - a one pager with some intro notes. Edited from CK-12
![]() Introduction to REDOX Practice - Some questions on this topic. From CK-12
Introduction to REDOX Practice - Some questions on this topic. From CK-12
SC2 - will be covered by class discussion and some notes from the board. It is very much about applying an understanding of electronegativity to oxidation and reduction. This application of your understanding will play a part to "make predictions" in SC6.
NOTE: The use of the terms Oxidation number and Oxidation state are used formally in SC5 for this unit. In many texts they are interchangable, however it is worth knowing the difference. Read the second paragraph of this article to recognise the difference. This will be important in answering questions (in the exam) using the correct format.
![]() Assigning Oxidation states's notes
Assigning Oxidation states's notes
![]() Assigning Oxidation state practice - Some questions on this topic
Assigning Oxidation state practice - Some questions on this topic
 Revision to this point. A one pager, should not be hard. Use to diagose any difficulty you are having.
Revision to this point. A one pager, should not be hard. Use to diagose any difficulty you are having.
![]() Assigning Oxidation states - 13.5 mins, by Tyler DeWitt. Slow, methodical, great.
Assigning Oxidation states - 13.5 mins, by Tyler DeWitt. Slow, methodical, great.
![]() Oxidising and Reducing Agents - 15 mins, by Tyler DeWitt. Watch and learn
Oxidising and Reducing Agents - 15 mins, by Tyler DeWitt. Watch and learn
![]() Balancing REDOX 1/2 Rn method - balancing by the half-reaction method, acidic environment only. Mainly an example of how to do it.
Balancing REDOX 1/2 Rn method - balancing by the half-reaction method, acidic environment only. Mainly an example of how to do it.
![]() Balancing by Half eqn - acidic environment WORKSHEET - error, will redo Note the answers to each of these can be obtained by control clicking each Q - super useful. These Questions are from the resource below
Balancing by Half eqn - acidic environment WORKSHEET - error, will redo Note the answers to each of these can be obtained by control clicking each Q - super useful. These Questions are from the resource below
 QUESTIONS (original site with the Qs in the handout above) Scroll down to the third set of examples ("balancing by the ion-electron method"), Click on any example, then "submit", and the solution is set out for you. AMAZING!
QUESTIONS (original site with the Qs in the handout above) Scroll down to the third set of examples ("balancing by the ion-electron method"), Click on any example, then "submit", and the solution is set out for you. AMAZING!
![]() Balancing REDOX reactions in acidic solutions - 15 mins, by Tyler DeWitt. Click here to see him do a practice problem. A more difficult question for advanced users is here
Balancing REDOX reactions in acidic solutions - 15 mins, by Tyler DeWitt. Click here to see him do a practice problem. A more difficult question for advanced users is here
![]() Balancing REDOX practice - a CK-12 Sheet with some practice questions.
Balancing REDOX practice - a CK-12 Sheet with some practice questions.
![]() Review for this unit. From CK-12. 25 Q's.
Review for this unit. From CK-12. 25 Q's.
2. Electrochemical cells
Unit 3 Topic 2 (Yr 11 Week 36 1 lesson)
NOTE: There is only one SC for this topic and it is a broad introduction to the idea of the link between chamcal energy and electrical energy in REDOX reactions and a few of the key terms.
![]() Electrochemistry and Electrochemical cells notes A simple two pager (reduce when photocopying) with an intro to electrochemical cells
Electrochemistry and Electrochemical cells notes A simple two pager (reduce when photocopying) with an intro to electrochemical cells
3. Galvanic cells
Unit 3 Topic 2 (Yr 11 Week 36,37 5 lessons)
![]() Galvanic cells notes - covers the basic theory of this topic. Heavily edited from CK-12. You need to be able to do the questions on the third page.
Galvanic cells notes - covers the basic theory of this topic. Heavily edited from CK-12. You need to be able to do the questions on the third page.
![]() Galvanic (Voltaic) cells - by Tyler again, 24 mins. Take your time, it is comprehensive, and simple.
Galvanic (Voltaic) cells - by Tyler again, 24 mins. Take your time, it is comprehensive, and simple.
![]() Galvanic cell QUIZ - edited from CK-12
Galvanic cell QUIZ - edited from CK-12
 Tutorial and simulation of Galvanic cell experiment - unbelieveable detail. On the left is a menu you can use to navigate. Work thru steps 1 and 2. Step 3 is the next topic.
Tutorial and simulation of Galvanic cell experiment - unbelieveable detail. On the left is a menu you can use to navigate. Work thru steps 1 and 2. Step 3 is the next topic.
4. Standard Electrode Potentials & Electrolytic cells
Unit 3 Topic 2 (Yr 11 Week 38 3 lessons)
![]() Electric Potential - notes. Edited from CK- 12. A brief introduction to the idea of electric potential
Electric Potential - notes. Edited from CK- 12. A brief introduction to the idea of electric potential
![]() Electric Potential - practice. Again an edited version of CK-12 questions. You should have no problems with these, checking for understanding.
Electric Potential - practice. Again an edited version of CK-12 questions. You should have no problems with these, checking for understanding.
![]() Standard Reduction Potentials - notes A 3 pager, heavily edited version of some CK-12 notes here.
Standard Reduction Potentials - notes A 3 pager, heavily edited version of some CK-12 notes here.
 Galvanic cells worksheet with answers
Galvanic cells worksheet with answers
![]() Galvanic cells worksheet. Stolen from somewhere, no answers
Galvanic cells worksheet. Stolen from somewhere, no answers
 SUMMARY of REDOX so far. Not certain about this sheet, but may be useful to check you know all the summary on here. Has a question at the end you should be able to do!
SUMMARY of REDOX so far. Not certain about this sheet, but may be useful to check you know all the summary on here. Has a question at the end you should be able to do!
![]() Electrolysis - notes. This is some of my writing and some borrowed stuff from CK-12. Has some questions at the end.
Electrolysis - notes. This is some of my writing and some borrowed stuff from CK-12. Has some questions at the end.
5. Chemical Equilibrium
Unit 3 Topic 1 (Yr 12 Week 1 3 lessons)
Start with the videos as introduction. The printout notes below cover most of the Success Criteria for this topic, but SC 19 and 24 will be done with classroom discussion/notes.
![]() Introduction to reversible reactions. nice and simple explaination of the idea. Nothing complicated.
Introduction to reversible reactions. nice and simple explaination of the idea. Nothing complicated.
 Introduction to Equilibrium. Video is 20 mins, but detailed and covers the ideas of why equilibium occurs and why dynamic equilibrium is.
Introduction to Equilibrium. Video is 20 mins, but detailed and covers the ideas of why equilibium occurs and why dynamic equilibrium is.
![]() Open, closed, isolated systems. This is all you need to know - assuming you understand it and can remember it.
Open, closed, isolated systems. This is all you need to know - assuming you understand it and can remember it.
![]() Equilibrium by Crash course Covers reversibility at the start (stop at 4 mins 14 sec). Le Chatelier is introduced after this, more suited to next topic.
Equilibrium by Crash course Covers reversibility at the start (stop at 4 mins 14 sec). Le Chatelier is introduced after this, more suited to next topic.
![]() Introduction to Equilibrium (notes and practice). A 3 pager - some from CK-12, mostly rewritten. Last page has some graphs for students to sketch (checking for understanding). Understanding this is very important for two reasons - it is an obvious "data skill" and it is a key interpreting skill which will surely be used on the exam. Many students think they know how to draw these graphs, and many students end up losing marks. Use the answer sheet below only when you are completly happy with your answer. Take your time. This is more than one lesson of work here.
Introduction to Equilibrium (notes and practice). A 3 pager - some from CK-12, mostly rewritten. Last page has some graphs for students to sketch (checking for understanding). Understanding this is very important for two reasons - it is an obvious "data skill" and it is a key interpreting skill which will surely be used on the exam. Many students think they know how to draw these graphs, and many students end up losing marks. Use the answer sheet below only when you are completly happy with your answer. Take your time. This is more than one lesson of work here.
![]() Answers to Introduction to Equilibrium The questions (some not all) have been answered and significant guidance shown about how to draw these graphs.
Answers to Introduction to Equilibrium The questions (some not all) have been answered and significant guidance shown about how to draw these graphs.
6. Factors that affect Equilibrium
Unit 3 Topic 1 (Yr 12 Week 2 3 lessons)
The notes below cover this topic very well, except that there is no mention of collision theory (SC 26) or the effect on Keq (SC27). The connection to collision theory should be obvious to you - higher concentations means more collisions and a higher rate of reaction (which affects equilibrium). The equilibrium constant connection is very briefly mentioned in the notes, and will be explained in the next section.
![]() Factors affecting Equilibrium (notes and practice). 8 pages. I spent a lot of time on this work, trying to make it simple and direct. read, summarise into your own notes. There are questions for checking for understanding.
Factors affecting Equilibrium (notes and practice). 8 pages. I spent a lot of time on this work, trying to make it simple and direct. read, summarise into your own notes. There are questions for checking for understanding.
![]() CLASSROOM VERSION Factors affecting Equilibrium (notes and practice). this is the version of the above notes I will use in class. We will use board notes and the guided practice.
CLASSROOM VERSION Factors affecting Equilibrium (notes and practice). this is the version of the above notes I will use in class. We will use board notes and the guided practice.
![]() Le Chatelier's Principle. By "Professor Dave", only 4 mins. Spot on for our course. Very direct and well explained.
Le Chatelier's Principle. By "Professor Dave", only 4 mins. Spot on for our course. Very direct and well explained.
 Another video by Science ready (HSC prep). 7.5 mins, I only checked out the first few minutes, but liked it.
Another video by Science ready (HSC prep). 7.5 mins, I only checked out the first few minutes, but liked it.
![]() Graphing Equilibria Worksheet.
Graphing Equilibria Worksheet.
 Worksheet, 2 pages. Has answers This is a very slightly edited copy from this site from a media site called tsfx. they provide resources for the VCE and HSC, surprised this was free?. Maybe a mistake, so copied a hard copy.
Worksheet, 2 pages. Has answers This is a very slightly edited copy from this site from a media site called tsfx. they provide resources for the VCE and HSC, surprised this was free?. Maybe a mistake, so copied a hard copy.
You should do questions 5 p1, 2 p1, 1 p2, 1 p3, 32 p4, 28b p5, 26 & 27 p6, 21 p8, 1b p9, 7b & 7c p11/12, 5 p12/13 from the booklet you received in class
7. Equilibrium Constants
Unit 3 Topic 1 (Yr 12 Week 1 3 lessons)
![]() The Equilibrium Constant (notes and practice). 3 pages with questions. Was a CK-12 but heavily heavily edited. Some easy questions, but check out the vid below for help with the harder ones.
The Equilibrium Constant (notes and practice). 3 pages with questions. Was a CK-12 but heavily heavily edited. Some easy questions, but check out the vid below for help with the harder ones.
 ANSWERS to the Qs in "The Equilibrium Constant" Worked answers by me. Have not been checked for errors. These include easy and moderate equilibrium Qs. Will give you some of the harder ones in class, or see resources listed a couple down.
ANSWERS to the Qs in "The Equilibrium Constant" Worked answers by me. Have not been checked for errors. These include easy and moderate equilibrium Qs. Will give you some of the harder ones in class, or see resources listed a couple down.
![]() Using Keq to calculate concentration changes. A video by "professor dave". Nice structure of his solutions, worth learning as his technique can be used for all types of concentration and Keq questions
Using Keq to calculate concentration changes. A video by "professor dave". Nice structure of his solutions, worth learning as his technique can be used for all types of concentration and Keq questions
 worksheet with equilibrium Qs Stole from Mark Iannone's site (see below). He has done answers and they are on this sheet underneath each question.
worksheet with equilibrium Qs Stole from Mark Iannone's site (see below). He has done answers and they are on this sheet underneath each question.
![]() ICE diagrams and Equilibrium calculations. by chad's prep, 23 mins. A bald headed guy teaching chemistry... can't go wrong! Just a video of Chad in front of a whiteboard, but I liked this as it was very well and simply explained.
ICE diagrams and Equilibrium calculations. by chad's prep, 23 mins. A bald headed guy teaching chemistry... can't go wrong! Just a video of Chad in front of a whiteboard, but I liked this as it was very well and simply explained.
![]() Keq worksheet (worksheet 11 from Mark Iaonne's site) and ANSWERS! Converted to word from Mark Iannone's site (see below). Amazing work by him
Keq worksheet (worksheet 11 from Mark Iaonne's site) and ANSWERS! Converted to word from Mark Iannone's site (see below). Amazing work by him
You should do questions 18 p1, 2 & 10 & 2 p3, 28a p5, 31 p7, 1a & c p9, 8 p10, 7a p11, from the booklet you received in class
Review of Equilibrium
 66 pages of Equilibrium Qs. and ANSWERS! by a teacher in British Columbia, Mark Iannone. Hat off to this guy, massive amounts of work. I will try and organise it a bit for this course (with some local files below... eventually), but all credit to Mark for this work!
66 pages of Equilibrium Qs. and ANSWERS! by a teacher in British Columbia, Mark Iannone. Hat off to this guy, massive amounts of work. I will try and organise it a bit for this course (with some local files below... eventually), but all credit to Mark for this work!
Data test practice
![]() Worksheet - data test style questions practice. 9 pages of questions. Covers redox, equil, and acid/base. This was difficult to compile, but should provide the type of thinking required to do well in most data tests.
Worksheet - data test style questions practice. 9 pages of questions. Covers redox, equil, and acid/base. This was difficult to compile, but should provide the type of thinking required to do well in most data tests.
 My answers to the OLD data test practice questions. This doc has not been updated yet to match the new worksheet above, it is for a similar but older version. Again, these are my answers and they may not be perfect - done under time pressure, so be nice if you find errors (and please let me know). Your teacher should explain the nature of marking in order to understand why these answers are written the way they are.
My answers to the OLD data test practice questions. This doc has not been updated yet to match the new worksheet above, it is for a similar but older version. Again, these are my answers and they may not be perfect - done under time pressure, so be nice if you find errors (and please let me know). Your teacher should explain the nature of marking in order to understand why these answers are written the way they are.
8. Acids and Bases - Bronsted-Lowry model
Unit 3 Topic 1 (Yr 12 Week 4 3 lessons)
There are lots of little ideas in this topic so a variety of notes are needed. The notes below cover this topic except for SC34 (amphoteric) which will be covered in class discussion. The notes are not in the same order as the SC, but do logically follow a sequences of ideas.
![]() Intro to acids and Bases. By Crash Course (11+ mins), general inro, covers key ideas for this topic without too much detail. HAs some real life implications.
Intro to acids and Bases. By Crash Course (11+ mins), general inro, covers key ideas for this topic without too much detail. HAs some real life implications.
![]() Acids and Bases - Introduction(notes and practice).
Acids and Bases - Introduction(notes and practice).
![]() Bronsted-Lowry acids/bases. Very specific short (3+ mins) covering Arhennius and Bronsted-Lowry ideas of what an acid or base is.
Bronsted-Lowry acids/bases. Very specific short (3+ mins) covering Arhennius and Bronsted-Lowry ideas of what an acid or base is.
![]() Cojugate Acids and Bases (notes and practice).
Cojugate Acids and Bases (notes and practice).
![]() Strengths of Acids and Bases (notes and practice).
Strengths of Acids and Bases (notes and practice).
![]() Strengths of Acids and Bases. By Fuseschool (5+ mins). Very uncomplicated, perfect for this point in time as it does not discuss Ka, just the idea of strong vs concentrated.
Strengths of Acids and Bases. By Fuseschool (5+ mins). Very uncomplicated, perfect for this point in time as it does not discuss Ka, just the idea of strong vs concentrated.
![]() Buffers. Crash Course vid (11+ mins). Good coverage, but longish.
Buffers. Crash Course vid (11+ mins). Good coverage, but longish.
From the booklet you received in class on Acids and Bases, you should do Q21 p1; Q7,Q22 p3; Q3 p4; Q12 p5; Q28 p6 (tough); Q6c),d) p15)
NOTE: I will teach pH, topic 10, before topic 9. The concept of pH is fairly central to volumetric analysis, so I believe it is important for students to have a good understanding of pH before volumetric analysis.
9. Volumetric Analysis
Unit 3 Topic 1 (Yr 12 Week 5/6 6 lessons)
Students will have little practical experience of titrations so the practical aspect will take some time with students - six lessons is not actually very much for this topic.
![]() Volumetric Analysis (notes and practice). Covers titrations and calculations of concentrations and titration curves. Notes were borrowed but heavily edited for this course.
Volumetric Analysis (notes and practice). Covers titrations and calculations of concentrations and titration curves. Notes were borrowed but heavily edited for this course.
Need to do a mandatory titration practical. Most texts will have a method.
![]() Performing a titration. Witts Uni video (6+ mins). Nice and simple for high school. Does not cover rinsing pipette or burette as prep for titration (see video below). I could not find a video which mentioned the need for waste beakers.
Performing a titration. Witts Uni video (6+ mins). Nice and simple for high school. Does not cover rinsing pipette or burette as prep for titration (see video below). I could not find a video which mentioned the need for waste beakers.
![]() Rinsing and filling a burette. A good video (4+ mins) except that the top of the burette is clearly too high. The volume marking on the burette should not be above eye level.
Rinsing and filling a burette. A good video (4+ mins) except that the top of the burette is clearly too high. The volume marking on the burette should not be above eye level.
From the booklet you received in class on Acids and Bases, you should do Q17,19 p1; Q8,10 p2; Q4,22 p3; Q27(b) p4; Q29(a) p6; Q31(c) p7; Q33 p8; Q8 (a,c) p10; Q4 p13/14; Q6 p15.
10. pH scale
Unit 3 Topic 1 (Yr 12 Week 7 3 lessons)
This topic discusses Kw before the course covers the Ka concept, which is the next topic. I think i will cover the simple pH calculation but then cover Ka and Kb, and come back to more complicated pH, pOH, and Kw calculations
 pH, Kw and pOH. Video (13+ mins) by Dr. Allison Soult of Uni. of Kentucky. Covers all 3 Success Criteria. Will use for notes. In case the course becomes unavailable, hard copy here
pH, Kw and pOH. Video (13+ mins) by Dr. Allison Soult of Uni. of Kentucky. Covers all 3 Success Criteria. Will use for notes. In case the course becomes unavailable, hard copy here
From the booklet you received in class on Acids and Bases, you should do Q16,17 p1; Q27(a) p4; Q26 p9; Q3(c) p10.
11. Dissociation Constants
Unit 3 Topic 1 (Yr 12 Week 8 3 lessons)
![]() Calculating Ka, Kb, pH, and pOH, (notes and practice). brief - 2 pages. Started with ck-12 but edited heavily. Some practice questions.
Calculating Ka, Kb, pH, and pOH, (notes and practice). brief - 2 pages. Started with ck-12 but edited heavily. Some practice questions.
![]() Ka and Kb worksheet. Stole this from "Mr Weathers" and edited slightly. Good sheet with some simple but comprehensive Ka and Kb Q's.
Ka and Kb worksheet. Stole this from "Mr Weathers" and edited slightly. Good sheet with some simple but comprehensive Ka and Kb Q's.
![]() Calculating pH from Ka. By The Science Classroom (6+ mins). Well set out and explained.
Calculating pH from Ka. By The Science Classroom (6+ mins). Well set out and explained.
![]() Challenge - Next level: Calculate the pH for a mixture of 50 mL of 0.2 M CH3COOH and 20 mL of 0.1 M NaOH (Ka for CH3COOH is 1.8 x 10-5). For a slightly harder question, calculate the pH at the equivelence point in a titration of 50 mL of 0.2 M CH3COOH with 0.1 M NaOH. The answer to the second question is here. This calculation is next level for us.
Challenge - Next level: Calculate the pH for a mixture of 50 mL of 0.2 M CH3COOH and 20 mL of 0.1 M NaOH (Ka for CH3COOH is 1.8 x 10-5). For a slightly harder question, calculate the pH at the equivelence point in a titration of 50 mL of 0.2 M CH3COOH with 0.1 M NaOH. The answer to the second question is here. This calculation is next level for us.
From the booklet you received in class on Acids and Bases, you should do Q18 p2; Q28(b) p5; Q31(a) p6; Q32 p7/8; Q3(b) p10; Q6(a,b) p12; Q7 P13.
12. Acid/Base Indicators Unit 3 Topic 1 (Yr 12 Week 9 3 lessons)
![]() Indicators (notes). brief - 2 pages. No questions.
Indicators (notes). brief - 2 pages. No questions.
![]() Questions (practice). Not complicated, fairly simple, 10 Q's.
Questions (practice). Not complicated, fairly simple, 10 Q's.
From the booklet you received in class on Acids and Bases, you should do Q2 p2; Q3 p3; Q29(b) p6; Q31(b) p7; Q4(d) p 14.
STUDENT EXPERIMENT:
Yr 12 Week 10 to 15(9 lsns in total)
![]() Student Investigation task sheet
Student Investigation task sheet
![]() Write a GREAT student experiment - WARNING - thisn is some solid reading and understanding! Guide to
Write a GREAT student experiment - WARNING - thisn is some solid reading and understanding! Guide to writing a great report getting a good mark on the report. this is the detail, and the ememplars below are examples.
![]() 2025 Syllabus - Student Investigation Exemplar - this is very similiar to the exemplar below as the changes to the criteria in the 2025 syllabus were not very extensive. However, redoing the exemplar provided me with an opportunity to redraft, so I think this version is written a liitle better.
2025 Syllabus - Student Investigation Exemplar - this is very similiar to the exemplar below as the changes to the criteria in the 2025 syllabus were not very extensive. However, redoing the exemplar provided me with an opportunity to redraft, so I think this version is written a liitle better.
![]() 2019 Syllabus Student Investigation Example
2019 Syllabus Student Investigation Example
Term 1 - Week 10
Unit 3 Revision
(3 lessons)
![]() Revision for Unit 3 - Q's from the public exam.
Revision for Unit 3 - Q's from the public exam.
UNIT 4
![]() Unit 4 Learning Goals and Success Criteria - Note these are a NEW version released 1st April.
Unit 4 Learning Goals and Success Criteria - Note these are a NEW version released 1st April.
1. Structure of Organic Compounds weeks 12 to 15 (7 lessons)
![]() Organic Chemistry Basics Background material you need to know. Read this, get some idea of the background knowledge you need, don't get depressed. Covers some of the language and basic knowledge (eg. condensed vs structural formulas) needed to begin Organic Chemistry.
Organic Chemistry Basics Background material you need to know. Read this, get some idea of the background knowledge you need, don't get depressed. Covers some of the language and basic knowledge (eg. condensed vs structural formulas) needed to begin Organic Chemistry.
![]() video worksheet - things to know. - SC 51. Complete this doc by watching the two videos below. The goal of this activity is to wrap your head around the language and the simple terms of organic chemistry. The worksheet contains the terms used in the Success Criteria (and a couple extra).
video worksheet - things to know. - SC 51. Complete this doc by watching the two videos below. The goal of this activity is to wrap your head around the language and the simple terms of organic chemistry. The worksheet contains the terms used in the Success Criteria (and a couple extra).
![]() Intro to Organic chemistry (Part 1) - by Melissa Maribel. Covers the language and names for this topic in two videos (see below). Use these videos to fill out the worksheet above
Intro to Organic chemistry (Part 1) - by Melissa Maribel. Covers the language and names for this topic in two videos (see below). Use these videos to fill out the worksheet above
![]() Intro to Organic chemistry (Part 2) - by Melissa Maribel. Ditto above
Intro to Organic chemistry (Part 2) - by Melissa Maribel. Ditto above
Now that your background knowledge is up to speed, let's look at the nomenclature (naming) of hydrocarbons, and structural isomers of hydrocarbons. Part of SC 52, and SC 53
![]() How to name hydrocabons - notes. My own guide to nomenclature of bydrocarbons, keeping the language as simple as possibe.
How to name hydrocabons - notes. My own guide to nomenclature of bydrocarbons, keeping the language as simple as possibe.
![]() Naming alkanes Part 1 By Professor Dave. Nice clear explanation - no point me doing this, couldn't do it any better.
Naming alkanes Part 1 By Professor Dave. Nice clear explanation - no point me doing this, couldn't do it any better.
![]() Naming alkanes Part 2. Second half of the above topic.
Naming alkanes Part 2. Second half of the above topic.
![]() Naming Alkenes and Alkynes. Prof. Dave.
Naming Alkenes and Alkynes. Prof. Dave.
![]() Naming Haloalkanes. Need only the first two mins of this video. Professor Dave again.
Naming Haloalkanes. Need only the first two mins of this video. Professor Dave again.
![]() Naming Hydrocarbons - worksheet
Naming Hydrocarbons - worksheet
 Naming Hydrocarbons - ANSWERS Did these last night.
Naming Hydrocarbons - ANSWERS Did these last night.
The link below is just for reference. It does have a good explaination of the first point of difference rule in nomenclature of hydrocarbons.
 the first point of diffrence rule. a simple explanation and how to implement it.
the first point of diffrence rule. a simple explanation and how to implement it.
SUMMARY Week 1 - you should be familiar with much of the necessary language used in organic chemistry, know how to name hydrocarbons, and identify and name structural isomers of hydrocarbons (up to 6C's)
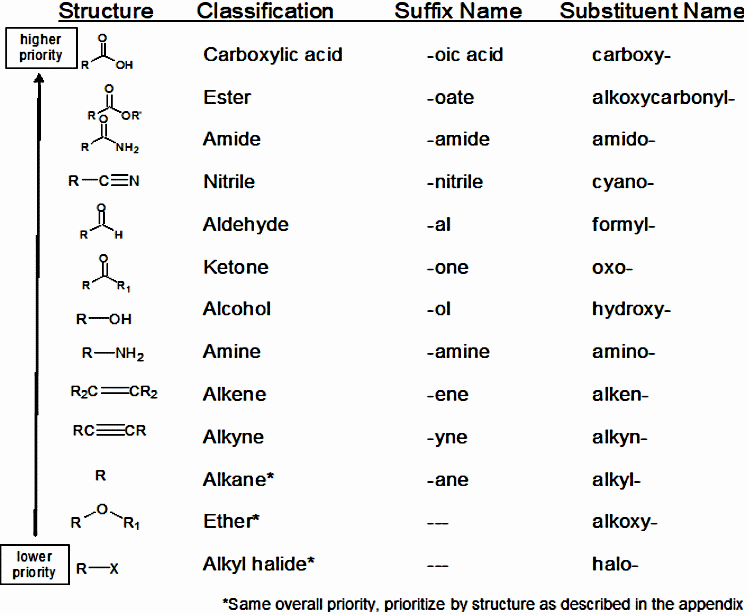
![]() Functional group nomenclature notes (all pages). Nine pages of pure bliss! Covers all the functional groups we need in our course. I wrote this over the hols and tried to simplify the language but still be accurate with IUPAC rules - there may be typos. You have these notes in your Notes pages in the OneNote, so only copy these if you want a copy as one whole document.
Functional group nomenclature notes (all pages). Nine pages of pure bliss! Covers all the functional groups we need in our course. I wrote this over the hols and tried to simplify the language but still be accurate with IUPAC rules - there may be typos. You have these notes in your Notes pages in the OneNote, so only copy these if you want a copy as one whole document.
![]() Naming Alcohols. Ignore the first two mins on haloalkanes, the rest is on alcohols. Professor Dave again.
Naming Alcohols. Ignore the first two mins on haloalkanes, the rest is on alcohols. Professor Dave again.
![]() Naming Amines. by Leah Fisch aka Lea4Sci.
Naming Amines. by Leah Fisch aka Lea4Sci.
![]() Naming Amides. by Leah Fisch aka Lea4Sci.
Naming Amides. by Leah Fisch aka Lea4Sci.
![]() Worksheet - Amines, Nitriles, Amides
Worksheet - Amines, Nitriles, Amides
![]() Naming Ketones. by Leah Fisch aka Lea4Sci.
Naming Ketones. by Leah Fisch aka Lea4Sci.
![]() Naming Aldehydes. by Leah Fisch aka Lea4Sci.
Naming Aldehydes. by Leah Fisch aka Lea4Sci.
![]() Worksheet - Ketones and Aldehydes
Worksheet - Ketones and Aldehydes
![]() Naming Esters. by Leah Fisch aka Lea4Sci.
Naming Esters. by Leah Fisch aka Lea4Sci.
![]() Naming Carboxylic acids. by Leah Fisch aka Lea4Sci.
Naming Carboxylic acids. by Leah Fisch aka Lea4Sci.
![]() Cis and trans nomenclature AGAIN. by ChemistNate. Watch until 5min 8secs, it covers E/Z nomenclature past this point. E/Z naming is used for more complex molecules, but our syllabus specifically mentions cis/trans for simple molecules.
Cis and trans nomenclature AGAIN. by ChemistNate. Watch until 5min 8secs, it covers E/Z nomenclature past this point. E/Z naming is used for more complex molecules, but our syllabus specifically mentions cis/trans for simple molecules.
![]() Cis and trans nomenclature. by Leah Fisch aka Lea4Sci. Also covers cyclic cis/trans which we do not need to cover. Check out from 9:52 onwards though.
Cis and trans nomenclature. by Leah Fisch aka Lea4Sci. Also covers cyclic cis/trans which we do not need to cover. Check out from 9:52 onwards though.
 Basic IUPAC Organic Nomenclature. Useful site. Firstly scroll down and click on the functional group you want to learn the rules for. Secondly - at each page scroll down and click the "practice questions". By the Chem Dept, Uni of Calgary (Canada).
Basic IUPAC Organic Nomenclature. Useful site. Firstly scroll down and click on the functional group you want to learn the rules for. Secondly - at each page scroll down and click the "practice questions". By the Chem Dept, Uni of Calgary (Canada).
2. Organic Macromolecules Weeks 16 - 19 (9 lessons)
![]() Advantages and disadvantages of Polymers Complete this. A worksheet to guide you in constructing some brief notes. Your text does not address this SC very directly and we could not find many specific references online. There is some information in this resource which may help constructing notes. Note that the cognitive verb of this SC is discuss... so we believe this is a broad, overall topic (general ideas) rather than something which requires a lot of specific chemistry knowledge. This will be a simple but frustrating task. Do it reasonably quickly, don't stress.
Advantages and disadvantages of Polymers Complete this. A worksheet to guide you in constructing some brief notes. Your text does not address this SC very directly and we could not find many specific references online. There is some information in this resource which may help constructing notes. Note that the cognitive verb of this SC is discuss... so we believe this is a broad, overall topic (general ideas) rather than something which requires a lot of specific chemistry knowledge. This will be a simple but frustrating task. Do it reasonably quickly, don't stress.
![]() Notes and Questions on Condensation Polymerisation Read and complete this worksheet. There is a lot of information here, and this has to be read slowly and with care. I recommend you highlight or summarise key points. The positive is that much of this information will also be useful later in this topic, so take you time to understand it now. This topic appeared so poorly done in your text and other texts that we wrote these notes for you. You do not need to "know" all of it, but you do need to understand all of it. You need to be able to do the questions with these notes. This will be difficult for you. I have included some videos below to support you - use them as this is an important topic. There are 3 videos on polymerisation of proteins, and two on polymerisation of polyesters (none of carbohydrates).
Notes and Questions on Condensation Polymerisation Read and complete this worksheet. There is a lot of information here, and this has to be read slowly and with care. I recommend you highlight or summarise key points. The positive is that much of this information will also be useful later in this topic, so take you time to understand it now. This topic appeared so poorly done in your text and other texts that we wrote these notes for you. You do not need to "know" all of it, but you do need to understand all of it. You need to be able to do the questions with these notes. This will be difficult for you. I have included some videos below to support you - use them as this is an important topic. There are 3 videos on polymerisation of proteins, and two on polymerisation of polyesters (none of carbohydrates).
The following three videos cover the condensation polymerisation of amino acids to make proteins. I have put them in the order I recommend you watch them. total of less than 12 mins.
![]() GCSE Science Chemistry (9-1 Triple) Amino Acids - by freesciencelessons, 3 mins. Watch for the big picture idea of how proteins are made, but don't focus on the detail, the other two videos below do a better job on the detail. An english school video.
GCSE Science Chemistry (9-1 Triple) Amino Acids - by freesciencelessons, 3 mins. Watch for the big picture idea of how proteins are made, but don't focus on the detail, the other two videos below do a better job on the detail. An english school video.
![]() Condensation polymerisation of amino acids - Start absorbing detail here. By maChemGuy (7 min). Very old school, uses a small white board and models of molecules. But it is simple and direct.
Condensation polymerisation of amino acids - Start absorbing detail here. By maChemGuy (7 min). Very old school, uses a small white board and models of molecules. But it is simple and direct.
![]() Amino Acids and Peptide Bonds - Condensation Reactions - by 5minschool, 2 + mins. Good backup and reinforcemnet of what you learnt in the above video.
Amino Acids and Peptide Bonds - Condensation Reactions - by 5minschool, 2 + mins. Good backup and reinforcemnet of what you learnt in the above video.
The following two videos cover the condensation polymerisation of diols (two alcohols groups) and dioic acids (two acid groups) to make polyesters. I have put them in the order I recommend you watch them. total of less than 13 mins.
![]() Condensation polymerisation polyesters - Excellent video, but very old school. Pay attention, this guy does a good job. By NobleChemGuy, 8 mins.
Condensation polymerisation polyesters - Excellent video, but very old school. Pay attention, this guy does a good job. By NobleChemGuy, 8 mins.
![]() Organic Condensation Polymers 1. Polyesters - Should reinforce everything you learnt in the first video. By FranklyChemistry, 5 mins
Organic Condensation Polymers 1. Polyesters - Should reinforce everything you learnt in the first video. By FranklyChemistry, 5 mins
![]() Notes on Protein structure Read these. These are note you may use to complete the worksheet below. see video below. These notes are in your OneNote, in your notes tab, as 2 c Protein structure.
Notes on Protein structure Read these. These are note you may use to complete the worksheet below. see video below. These notes are in your OneNote, in your notes tab, as 2 c Protein structure.
![]() Worksheet - to write your own notes, and two questions Complete this worksheet. The worksheet is in your OneNote, in your homework tab, as Wk 3 2 c Summary of Protein structure.
Worksheet - to write your own notes, and two questions Complete this worksheet. The worksheet is in your OneNote, in your homework tab, as Wk 3 2 c Summary of Protein structure.
![]() Protein structure. by Prof Dave. Very good, simple info for understanding this topic and making your notes. He starts with some nomenclature you need - the four types of structure follows.
Protein structure. by Prof Dave. Very good, simple info for understanding this topic and making your notes. He starts with some nomenclature you need - the four types of structure follows.
![]() Guide to making notes on Proteins as Enzymes (SC 59) - use this guide to Complete some notes on proteins as enzymes. Need the QCE Chemistry Unit 4 text book.
Guide to making notes on Proteins as Enzymes (SC 59) - use this guide to Complete some notes on proteins as enzymes. Need the QCE Chemistry Unit 4 text book.
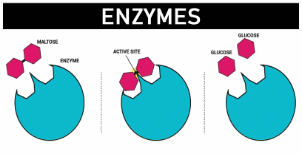
 Proteins as Enzymes - by Libretexts. Has a good description of how the structure of the R groups of amino acids influences enzyme action. Stop at "cofactors" - gets too detailed.
Proteins as Enzymes - by Libretexts. Has a good description of how the structure of the R groups of amino acids influences enzyme action. Stop at "cofactors" - gets too detailed.
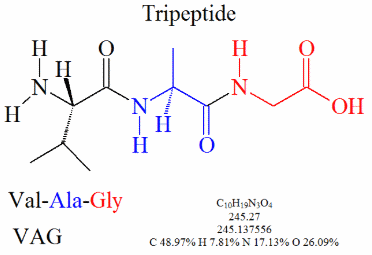
 Identifying the AAs in a polypeptide. The last five pages of this pdf contain one polypeptide per page. The previous pages show the structure of many Amino Acids. For each of the polypeptides identify the Amino acids within it, and list the number of water molecules produced by the condensation reactions.
Identifying the AAs in a polypeptide. The last five pages of this pdf contain one polypeptide per page. The previous pages show the structure of many Amino Acids. For each of the polypeptides identify the Amino acids within it, and list the number of water molecules produced by the condensation reactions.
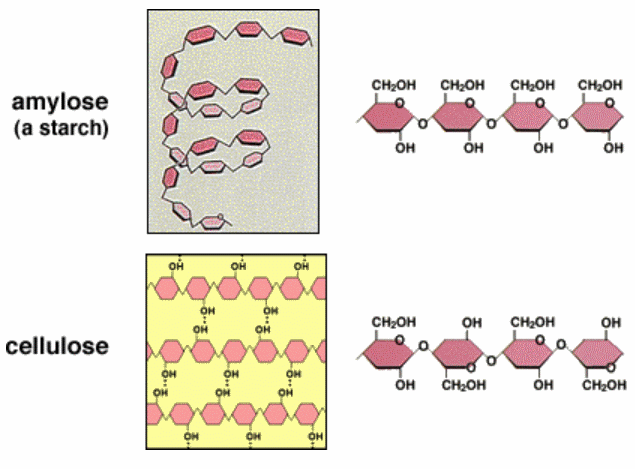
![]() Carbohydrates - Notes and Qs - covers SC 61 to 63. Summarise or highlight the notes, and answer the Qs
Carbohydrates - Notes and Qs - covers SC 61 to 63. Summarise or highlight the notes, and answer the Qs
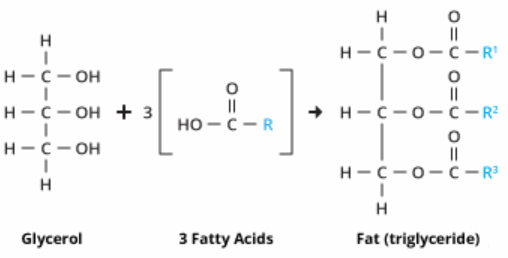
![]() Fats and Oils - guide to notes - covers SC 64 to 64. Guide and Qs only - use these as a guide to making your notes form the text. There is an intro though, and some additional information about hard water which is not in your text.
Fats and Oils - guide to notes - covers SC 64 to 64. Guide and Qs only - use these as a guide to making your notes form the text. There is an intro though, and some additional information about hard water which is not in your text.
![]() Addition polymerisation - Notes and Questions . Highlight the notes according to the SC 66 and 67. The questions at the end of the notes focus on the SC and are great exam practice for you.
Addition polymerisation - Notes and Questions . Highlight the notes according to the SC 66 and 67. The questions at the end of the notes focus on the SC and are great exam practice for you.
 Multiple choice quiz - covers SC 66 and 67. Edited - from an organisation called NAGWA.
Multiple choice quiz - covers SC 66 and 67. Edited - from an organisation called NAGWA.
RESEARCH ASSIGNMENT:
Yr 12 Week 15 to 24(9 lsns in total)
![]() Research Investigation exemplar (link to article on my Data Analysis and report writing page) I wrote this one for fun :-( Read the disclaimer on the webpage.
Research Investigation exemplar (link to article on my Data Analysis and report writing page) I wrote this one for fun :-( Read the disclaimer on the webpage.
![]() Simple Guide to a Research Investigation - A colleague wrote this one. Obviously the key is to get data, but once that is done, this guide breaks it down into simple achievable steps.
Simple Guide to a Research Investigation - A colleague wrote this one. Obviously the key is to get data, but once that is done, this guide breaks it down into simple achievable steps.
![]() How to write a Research Investigation. No idea where this came from, but it is teacher generated. Get your data and research question sorted. Then read and follow this when you start writing.
How to write a Research Investigation. No idea where this came from, but it is teacher generated. Get your data and research question sorted. Then read and follow this when you start writing.
3. Organic Reactions and Reaction Pathways Weeks 20 to 22 (6 lessons)
Notes We will start with going through the Success Criteria. SC 68 to 70 are a little more general and we will discuss their meaning in class and make notes. SC 71 to 75 will be completed on the reaction map I printed out (see below), as well as with some brief notes.
Activity I will give you a copy of the pic on the right (see doc below). It is a map of all the reactions in this section, including the reactions listed in SC 71 to 75. On your copy, circle all the reactions listed in SC 71 to 75, and identify them on your reaction map with appropriate labels. Write the conditions and any catalysts/reactants into the map. These should be written on the arrow. I will show you an example of this (nitriles). This is an exercise in you understanding how these reactions combine together... big picture and familiarity... we will go into the specifics of each reaction after this.
ActivityThe next step is to make notes on each reaction type. These are covered in your text book. Make notes about all the combustion reactions, then the substitution reactions, then all the addition reactions, then the oxidation reactions of alcohols.
![]() Reaction pathway map. The one on the right.
Reaction pathway map. The one on the right.
Links to reaction types. Below are links to a chemguide site. Each link covers a "type" of reaction on your reaction map and contains links to specific examples. Generally there are more examples on this page than are listed in you reaction map find the ones on your map and click them. This site provides information which is more advanced than you need. Get the basic reaction pathway details (reaction conditions, example) only. You can ignore the reaction mechanism information.
 Substitution Reactions. These are called nucleophilic substitution reactions (or more technically SN1 and SN2).
Substitution Reactions. These are called nucleophilic substitution reactions (or more technically SN1 and SN2).
 Elimination Reactions. The first link on this page is all you need as we only have one elemination reaction listed on our map. However the next two may be worth reading so you understand some of the symetry detail, and the difference between elimination and substitution. These are also commonly referred to as E1 and E2 reactions.
Elimination Reactions. The first link on this page is all you need as we only have one elemination reaction listed on our map. However the next two may be worth reading so you understand some of the symetry detail, and the difference between elimination and substitution. These are also commonly referred to as E1 and E2 reactions.
 Addition reactions of Alkenes. The second and fourth link are reactions listed in our reaction map. Then go to the sixth link "Why unsymmetric alkenes are a problem . . ." This link covers unsymetrical alkenes - you will need to know Markovnikov's rule - it is explained at this link.
Addition reactions of Alkenes. The second and fourth link are reactions listed in our reaction map. Then go to the sixth link "Why unsymmetric alkenes are a problem . . ." This link covers unsymetrical alkenes - you will need to know Markovnikov's rule - it is explained at this link.
4. Properties and trends Week 23 (3 lessons)
This part of the website is underdeveloped... see the image on right!!!! Luckily, this topic is covered pretty well in our textbook p28 - 40. This topic is very big on understanding... and if you do understand, there is NOT a lot of memory work.
5. Chemical Synthesis Weeks 25 and 26 (6 lessons)
![]() Introduction to Synthesis. Mainly for understanding but use the two Qs to make notes from this page.
Introduction to Synthesis. Mainly for understanding but use the two Qs to make notes from this page.
![]() Calculations on limiting reagent and Yield. This covers the last SC in this topic. We are covering it now so we can practice these calculations throughout the unit. Has some examples and some Qs for you.
Calculations on limiting reagent and Yield. This covers the last SC in this topic. We are covering it now so we can practice these calculations throughout the unit. Has some examples and some Qs for you.
There are four specific examples of synthesis you need to be able to remember. The first two - Synthesis of Ammonia and Sulphuric acid are the more difficult as they involve equilibrium considerations. The next two - Biodiesel and Ethanol, involve more memory work, but are not complex.
![]() Synthesis of Ammonia Notes and some questions to help your understand the key points.
Synthesis of Ammonia Notes and some questions to help your understand the key points.
![]() Synthesis of Sulphuric Acid Notes and some questions to help your understand the key points.
Synthesis of Sulphuric Acid Notes and some questions to help your understand the key points.
![]() Notes on the synthesis of Biodiesel. No questions on this one. We will look at the SC - there are four SC which mention biodiesel - and use them as a guide to what notes we need for study.
Notes on the synthesis of Biodiesel. No questions on this one. We will look at the SC - there are four SC which mention biodiesel - and use them as a guide to what notes we need for study.
![]() Notes on the synthesis of Ethanol. No questions on this one. We will look at the SC - there are three SC which mention ethanol - and use them as a guide to what notes we need for study.
Notes on the synthesis of Ethanol. No questions on this one. We will look at the SC - there are three SC which mention ethanol - and use them as a guide to what notes we need for study.
![]() General video on Hydrogen fuel cells. 5+ mins. An IB video. Note the methanol version is not in our course. Uses the term PEM (correctly), which in our course is refered to as "acidic conditions". This is explained in the video however, and in the info with the vid. Good understanding and visuals of the equations. Check the info with the video, there is a balancing error at 4 mins 27 sec.
General video on Hydrogen fuel cells. 5+ mins. An IB video. Note the methanol version is not in our course. Uses the term PEM (correctly), which in our course is refered to as "acidic conditions". This is explained in the video however, and in the info with the vid. Good understanding and visuals of the equations. Check the info with the video, there is a balancing error at 4 mins 27 sec.
![]() Discussion of the voltages of hydrogen fuel cells. 8+ mins, but you need only the first 4 mins or so. Starts blurry but clears up at the 1 min mark, when we need to see the detail. Goes through the Cell voltage angle, which is a good link back to redox chemistry - seems an obvious way to link the two topics together. There is a Q with the following notes also covering this idea.
Discussion of the voltages of hydrogen fuel cells. 8+ mins, but you need only the first 4 mins or so. Starts blurry but clears up at the 1 min mark, when we need to see the detail. Goes through the Cell voltage angle, which is a good link back to redox chemistry - seems an obvious way to link the two topics together. There is a Q with the following notes also covering this idea.
![]() Notes on Hydrogen Fuel cells. Has two Qs.
Notes on Hydrogen Fuel cells. Has two Qs.
That more or less ends the synthesis topic - except for the mention of the synthesis of Hydrogen which is mentioned very briefly in SC 70. Steam (H2O)reacts with methane (CH4) and oxidation of the Carbon occurs to produce CO and Hydrogen gas. Further oxidation of the CO to CO2, produces more hydrogen.
6. Green chemistry and Molecular manufacturing Weeks 27 (3 lessons)
This is covered pretty well in our main textbook. We will look closely at the Success Criteria and make some notes directly from the text, along with answering some Qs from it.
21. Analytical Techniques Week 28 and 29 (5 lessons)
This part of the website is underdeveloped... see earlier image on right!!!!

CHEMISTRY: Downloads and links
 Periodic Table - see the top tabs
Periodic Table - see the top tabs
 Periodic Table - see History & Trends tabs
Periodic Table - see History & Trends tabs
![]() Balancing Chemical Equations Video 1
Balancing Chemical Equations Video 1
![]() Balancing Chemical Equations Video 2
Balancing Chemical Equations Video 2
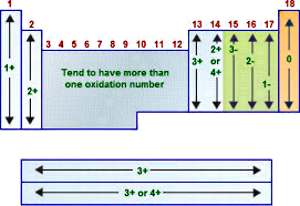
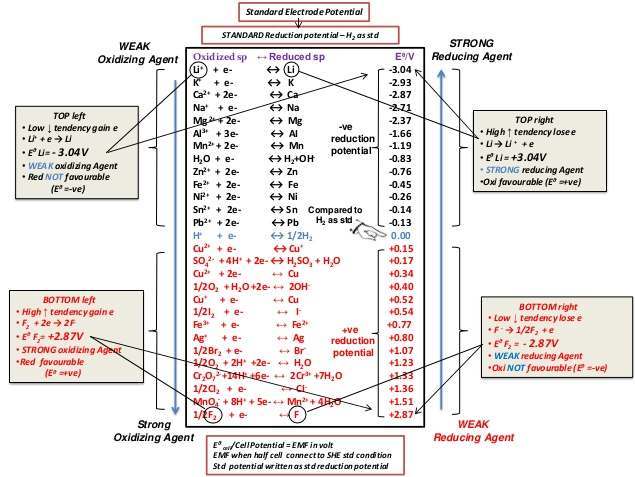
How to avoid a Research Assignment...
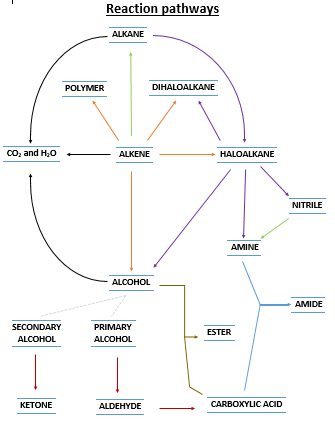
I will give you a copy of this in class for rough note taking. There is a doc listed on the left whigh can be a neater copy for your study notes.